Quantitative Protein Mass Spectrometry to Assess Plasma Proteins Involved in Coagulation and Fibrinolysis

Half of all patients referred to a tertiary center for suspected bleeding disorders can’t be diagnosed with current diagnostic assays, which reveals the limitations of these assays. Hemostasis laboratories use screening assays that measure coagulation factor levels (APTT, PT, fibrinogen), but these aren’t precise enough to predict the interindividual variability in bleeding phenotype. Different tests […]
Read moreKidney organoid and scaffold research

In our research group we combine two complementary research themes to generate insight in the development of alternative, innovative strategies for tissue engineering: 1) kidney scaffolds and 2) stem cells. Our approach ultimately strives to overcome the shortage of human donor organs by using the patient’s own cells for kidney bioengineering. In the past couple […]
Read moreIslet group research

The insulin-producing beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas play a key role in all types of diabetes mellitus. The islets of Langerhans are the main focus of both clinical and basic research projects. The Islet group started in 2006 when a human islet isolation laboratory was established in the Leiden University […]
Read moreRole of brown adipose tissue in metabolic health

Brown adipose tissue has recently emerged as an important player in energy metabolism as it dissolves high amounts of lipid and glucose into heat. Therefore, brown adipose tissue is now being considered as a novel target to combat obesity and related diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. In our group, we aim […]
Read moreVascular Nephrology Group Research

The Vascular Nephrology Group was initiated by Anton Jan van Zonneveld and Ton Rabelink in 2004 and research topics are centred around the understanding and clinical translation of molecular mechanisms in vascular injury and repair, secondary to adverse metabolic- or hemodynamic risk factors such as encountered in diabetes, chronic kidney disease or kidney transplantation. The […]
Read moreThe role of coagulation factors in cancer and malignancy-associated thrombosis.

It is now known that cancer and blood clotting are tightly connected. Cancer cells vastly upregulate specific blood clotting factors and this is believed to result in the formation of unwanted blood clots in veins and the lungs, often leading to fatal, thrombotic complications in cancer patients. In addition, my own works has shown that […]
Read moreNeuroimmune guidance cues, MicroRNAs & Inflammatory responses: Sex differences in CardioVascular Diseases
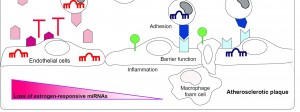
Cardiovascular disease remains number one cause of premature death in women. Despite advances in the diagnosis, prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease, the risk of coronary artery disease in women increases dramatically after menopause. In this MISs-CVD project we aim to better understand sex-specific biology in the vessel wall. Specifically, sex-biased non-coding microRNAs that can […]
Read morePersonalized gene-targeted treatment strategies for von Willebrand disease

Current therapies for patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) include the use of desmopressin (DDAVP) or the administration of von Willebrand Factor (VWF) concentrates. In this collaboration with Erasmus MC (group of Prof. Leebeek) and Amsterdam UMC (group of Prof. Voorberg) we will (further) investigate whether we can correct the phenotype of VWF mutations by […]
Read moreDiagnostic management of venous thromboembolism

Signs and symptoms of acute venous thromboembolism (VTE) are notoriously nonspecific. Therefore, diagnostic management algorithms have been developed, consisting of a clinical decision rule (CDR), D-dimer testing and imaging tests, that allow safe diagnostic management and the exclusion of VTE in clinical practice. However, several challenges still remain: adherence to the diagnostic algorithms, accurate diagnosis […]
Read moreMonocyte conversion in patient cohorts

Monocytes are circulating leukocytes important in both innate and adaptive immunity. In humans, three different monocytes have been identified, based on their phenotypic expression of CD14 and CD16. These different subsets have been shown to exert different functions, where the non-classical monocyte is thought to contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and high numbers of […]
Read moreTolerogenic Cellular Immunotherapy

We have established methods to generate and characterize tolerogenic antigen presenting cells (dendritic cells and macrophages) in human and rat and applied these in experimental renal transplantation models. In vitro experiments with human monocyte-derived DC concentrate on the immune regulatory mechanisms of corticosteroids and have a established a differential regulation of cytokines from the IL-12 […]
Read morePost-transcriptional investigation of platelet aggregation

Platelets represent the second most abundant cell-type in human blood. The primary function of platelets is to survey blood vessels for injury, and to instigate coagulation processes at sites where the endothelium has become damaged. Aside from their haemostatic task, they are also regenerative in nature, as instrumental regulators of angiogenic processes that ultimately serve […]
Read moreLimiting pro-atherogenic macrophage formation: Taming Quaking and inflammation

A critical part of the RNAissance (a period in which the realization has developed that RNA is not merely an intermediate) is the invention of commercial microarrays (link to de Bruin et al., European Heart Journal, 2016). This technological advancement, albeit slightly dated now in 2016, enabled scientists worldwide to identify changes in coding-gene expression […]
Read morePost-transcriptional regulation as a key driver of intrinsic kidney regeneration

The increasing prevalence of noncommunicable diseases such as diabetes and hypertension have caused an alarming increase in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Augmenting the capacity of the kidney to regenerate intrinsically is a major challenge that could prevent irreversible kidney failure. While the cells of the Renin-Lineage (CoRL) play a critical role in regulating blood pressure […]
Read moreThe role of human genetic variations in neuronal guidance cues in premature atherosclerosis

The molecular basis of premature cardiovascular disease (CVD) is incompletely understood. Adverse endothelial monolayer permeability and leukocyte migration are key features in the onset and progression of atherosclerosis. The ligands and receptors of the Neuronal Guidance Cues (NGCs) have been shown to play a potent and rate-limiting role in atherogenesis in mouse model. Human validation […]
Read moreThe endothelial compartment as disease modifier in bleeding disorders

This research is part of the project “SYMPHONY: Orchestrating personalized treatment for patients with bleeding disorders”. This part of the project (WP12) focuses on the cellular mechanisms behind interindividual variation in bleeding phenotypes between patients with bleeding disorders. The hypothesis of this study is that genetic variations in secretory pathway components of platelets and endothelial […]
Read moreBiomarkers of renal inflammation and chronic transplant failure

In view of the importance of local immune and inflammatory processes, we have developed immunohistochemical methods to characterize and quantify myeloid subsets in human renal biopsies (pre-transplant, protocol- and rejection biopsies). We have been able to demonstrate that the composition of infiltrate has an impact on the long term function of transplanted organs. Moreover we […]
Read moreLong noncoding RNAs as a determinant of microvascular stability in chronic kidney disease

Irrespective of the etiology, the common pathway in the pathology of Chronic kidney disease (CKD) involves: glomerular sclerosis, tubulointerstitial fibrosis associated with inflammation, myofibroblast proliferation and activation, extracellular matrix accumulation and tubular atrophy. The loss of the peritubular capillary network (rarefaction) is directly correlated with the severity of fibrosis, and the extent of rarefaction has […]
Read moreNeuroimmune guidance cues to combat atherosclerosis
Despite significant therapeutic advancements, cardiovascular disease persists to be a worldwide leader of morbidity and mortality. Atherosclerosis, a main driver of cardiovascular disease, progresses following the transmigration of lipids and inflammatory cells through the vascular endothelium into the vascular wall. Therefore, adverse endothelial monolayer permeability and leukocyte migration are key features in the onset and […]
Read morePlatelets are instrumental in the mobilization and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells at the site of a vascular injury.

Activated platelets accumulate at the site of a vascular injury, where they support the escape of the hematopoeitic stem cells (HSCs) from flow and provide a pro-angiogenic niche (fertile-soil). Upon immobilization of the HSCs, they become subject to shear stress, which leads to the expression of the receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), […]
Read moreOptimal therapeutic management of acute and chronic venous thromboembolism

In recent years, Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin-k antagonists as treatment of choice for venous thromboembolism for 3 main reasons. First, DOACs were shown to be associated with less major bleeding than conventional anticoagulants. Second, DOACs have only few interactions with other drugs and food and third, DOACs dot need routine blood […]
Read morePlatelets plug a breached vessel wall, but may support the activation of coagulation under AF-conditions.

Under normal physiological conditions, platelets support the integrity of the endothelial cell monolayer. Furthermore, when the vessel wall is breached, normal platelets adhere to the exposed extracellular matrix and form the first line of defence, thus preventing excessive blood loss. In patients with atrial fibrillation, systemic activation of platelets coincides with hypercoagulability. Our data show […]
Read moreProtecting the endothelium: Post-transcriptional control of barrier function by Quaking

All blood vessels are lined with a single layer of endothelial cells (ECs), which form a vital barrier between the blood and underlying tissue. The control of the EC barrier is critical to maintain vascular stability and retain circulating fluids, solutes, proteins and cells within the vasculature. Excessive vascular permeability plays a key role in […]
Read moreTransition from acute to chronic thrombosis

One of the most feared complications of venous thromboembolism (VTE) are permanent hemodynamic changes due to unresolved thrombi or vascular damage caused by thrombosis. Half of patients treated for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) suffer from post-thrombotic syndrome and post-PE syndrome, respectively. The most severe presentation of the post-PE syndrome is chronic […]
Read moreCharacterization of endothelial colony forming cells of von Willebrand disease patients

The endothelium is a key player in cardiovascular and inflammatory disorders. A number of pro-thrombotic and pro-inflammatory mediators are stored in endothelial cell specific organelles known as the Weibel-Palade bodies (WPBs). A major constituent of WPBs is the multimeric glycoprotein von Willebrand factor (VWF) which arrests bleeding by recruiting blood platelets to sites of vascular […]
Read moreCirculating noncoding RNA as posttranscriptional determinant of cardiovascular complications in CKD

Chronic kidney disease (CKD), with diabetes mellitus predominating its etiology (Diabetic nephropathy), is a leading cause of death due to cardiovascular disease. It is becoming increasingly apparent that global regulation of critical processes occur at the post-transcriptional level by non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs, including microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs). Despite their intracellular functions, ncRNAs are also […]
Read moreComplement in ischemia/reperfusion injury and complement-mediated renal diseases

Ischemia/reperfusion is an early and inevitable process organ transplantation, and the innate immune system has been implicated as a critical mediator of injury. In a combination of clinical, experimental and in vitro experiments we have established a new role for Mannan Binding Lectin (MBL), the initiator of the lectin pathway of complement. Recipients with low […]
Read moreDisease in a dish: Modelling Von Willebrand disease with patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells

Blood outgrowth endothelial cells (BOECs), also indicated as endothelial colony forming cells (ECFCs), are being used in our lab and by others as an endothelial cell model to study Von Willebrand disease (VWD) and Von Willebrand factor (VWF). To overcome some of the shortcomings of this model, among which the low success rate of isolation […]
Read moreThe glomerular endothelial surface glycocalyx in early diabetes

The glycocalyx is a network of long-unbranched polysaccharides projecting from the surface of endothelial cells which lines blood vessels. Although the endothelial glycocalyx has been identified morphologically several decades ago and a number of physiological and pathological functions have been attributed, the exact molecular composition and function remains largely unknown. In our group we focus […]
Read moreAssembling the molecular machinery of coagulation: learning from the adaptive evolution of snake venom proteins

Hemostasis is regulated by the activity of macromolecular enzyme-cofactor complexes that require a negatively charged membrane surface for their assembly. Apart from spatially organizing the coagulation reactions upon vascular injury, the phospholipid surface-driven complexation also profoundly enhances the catalytic rate of protein substrate conversion. Suggestions as to how the membrane surface propagates the coagulation reactions […]
Read moreThe role of Quaking (isoforms) in platelet aggregation
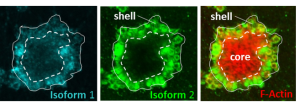
In the process of platelet aggregation, the forming thrombus develops a very distinctive architecture, with a core of densely packed platelets, overlaid by a shell of loosely packed, adherent platelets. The core of the thrombus is consolidated with filamentous actin (F-Actin; red) which gives the thrombus its strength to withstand blood flow. We have studied […]
Read moreGenetics of the Metabolic Syndrome
The genetics of the metabolic syndrome is addressed using a systems biology based approach encompassing a combination of in depth phenotypic characterization of patients and controls with bioinformatics/biostatistics techniques. We study well-defined patient groups which have undergone very specific interventions (i.e. bariatric surgery or prolonged caloric restriction) and determine the effects on plasma and tissue […]
Read moreVaattoegang/ Vascular access

Vascular access dysfunction remains the Achilles’ heel of hemodialysis, leading to substantial morbidity and mortality. The LUMC has an extensive track record in the field of vascular access, which is organized from without our expertise center, in which nephrologists, vascular surgeons, biologists, technicians and engineers are working together. Our research includes preclinical studies on the […]
Read moreIdentification of novel inherited risk factors for venous thrombosis using NGS

Historically, monogenetic disorders have greatly helped the unravelling of biological pathways following the identification of novel genes. Recently, important technological advances have given geneticists and biologists remarkable opportunities. While a few years ago small families with only a few affected individuals could not provide breakthroughs, this has changed dramatically over the past year, especially through […]
Read moreLowering von Willebrand factor as a therapeutic approach to reduce the risk of thrombosis
Cardiovascular disease is one of the leading causes of death. Individuals with high von Willebrand factor (VWF) levels have an increased risk of coronary heart disease, ischemic stroke, venous thrombosis, and also cardiovascular mortality. Genetic variations in VWF have been associated with VWF levels and increased risk of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke. The […]
Read moreCancer and thrombosis

Cancer and incident thrombosis are very much associated. One the one hand are patients with cancer at higher risk of developing venous thromboembolism due to procoagulant proteins produced by cancer cells, high frequency of surgical procedures and period of immobility, pro-thrombotic chemotherapy and local compression of veins by tumour mass. On the other hand, coagulation […]
Read moreA novel cofactor-based procoagulant protein as bypassing agent for hemophilia
Hemophilia is an X-linked bleeding disorder that results from a deficiency or defect in blood clotting factor VIII (hemophilia A) or factor IX (hemophilia B). Hemophilia patients are treated with protein infusions to replace the defective or missing protein. Unfortunately, up to 30% of patients develop an immune response to the infused protein, which renders […]
Read moreThe PHArmacogenomic Study of Statins in the Elderly at risk for cardiovascular disease (PHASE)

The PHArmacogenomic Study of Statins in the Elderly at risk for cardiovascular disease (PHASE) is a genome-wide association study (GWAS) performed in the participants of the PROspective Study of Pravastatin in the Elderly at Risk (PROSPER), a large prospective European multi-national placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial with 5804 participants. With the GWAS in PHASE (EU project […]
Read moreThe Netherlands Epidemiology of Obesity study

The Netherlands Epidemiology of Obesity Study (NEO) is a population-based cohort study in overweight and obese (BMI at least 27 kg/m2) men and women aged 45 to 65 years from the Leiden region in The Netherlands. NEO is designed to study the pathways that lead to common diseases and conditions in overweight and obese individuals. […]
Read moreINCOAG: Whole-blood coagulation profile

Cardiovascular diseases remain the principal cause of death and ischemic heart disease and stroke comprise >50% of total cardiovascular mortality. Arterial thrombosis is the principal cause of acute ischemic cardiovascular death due to occlusion of coronary or carotid arteries leading to myocardial infarction and stroke, respectively. Thrombosis in the venous system is also an important […]
Read moreMaintaining healthy perivascular stromal cells: Zooming in on vascular smooth muscle cell and pericyte biology

My first scientific love, the vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMCs) is the most abundant cell type in the artery wall. In healthy arteries, VSMCs serve to maintain vascular tone, with intrinsic and extrinsic factors influencing their control of blood flow and blood pressure in the coronary and peripheral arteries. Upon vascular injury, VSMCs undergo a […]
Read moreE-coagulation: applied coagulation systems biology to accurately assess the hemostatic balance of individual patients

The blood coagulation system consists of an intricate set of reactions that protect the body from bleeding and thrombosis. In general, the system is well-balanced and excessive bleeding or runaway coagulation in an individual are not daily events, but the life-time risk of a single event is nevertheless high. In cases with profound inherited or […]
Read moreSystems biology of the Metabolic Syndrome

In addition to bioinformatics and biostatistics we apply functional genetics in combination with mathematical modeling approaches to understand the fluxes of carbohydrates and lipids in vivo. In addition, we are addressing the relation between energy intake and energy expenditure. For example, we are determining the amount of energy that is expended due to movement and […]
Read morePathology of the Metabolic Syndrome

In close collaboration with the department of Immunohematology and Blood transfusion we are investigating the role of the adaptive immune system in adipose tissue in the development of obesity and its pathological consequences. We are specifically focusing on the role of antibodies and their effector systems in immune cells associated with adipose tissue.
Read more